What is bee pollen?
Bee pollen is the male seed of the flower blossom, which is collected by the honey bees. It represents the main food source for the bees and contains proteins, minerals, fats, and other substances that are essential for their survival.
By collecting the nectar from the flowers, honey bees pollinate them. Without pollination, humanity would live only for no more than 4 years, they say Einstein said that.
You don’t have to be a genius to realize that without pollination, flowers disappear, insects disappear, animals and humans disappear. In the USA and some other countries, peasants pay the beekeepers for their bees’ pollination services.
Bee pollen is not the pollen that is carried by the wind and causes allergies. Actually, if you suffer from these allergies, there are therapists that recommend small doses of raw bee pollen, which will act like a vaccine, and help the body protect itself against the symptoms of hay allergy (the pollen taken by the wind). Or, why not, try bee venom therapy. It has a very good rate of success.
How is the pollen gathered?

The bee lands on the flower’s blossom and touches the stamen. Its body is covered with pollen dust. The bee uses the hind legs to compress the pollen into the pollen baskets. It moistens the pollen with secretions from its mouth, which helps the pollen cling together.
A load of pollen has like 8 mg and for this, a bee has to visit almost 200 flowers. A honey bee makes approximately 10 trips a day to gather pollen. Once the bee enters the hive, the pollen is removed from the rear legs by a spike on the mid legs and placed in cells. Honey is added to maintain pollen quality.
How is bee pollen stored?
Fresh bee pollen The freshly collected bee pollen contains about 20–30 g of water per 100 g. (It depends a lot on the atmospheric conditions.) This has high humidity, and it’s an ideal medium for bacteria and yeast. This is why the pollen should be harvested daily and placed directly in the freezer. In two days, all pest insects will be killed. After the thawing, the bee pollen can be kept only for a few hours.
Dried bee pollen is made through a process of drying and purifying. After that, the water content would be of 6 g per 100 g pollen. Of course, during these processes, there will be losses of vitamins ( pro-vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E and β-carotene) and some other important nutrients.
Limits of storage:
Dried pollen stored at room temperature: 12 months
Dried pollen packed in vacuum: 24 months
Frozen fresh pollen stored in the freezer: 12 months
What’s the composition of bee pollen?
The composition varies according to the flower of provenience. Generally, it contains: proteins, lipids, dietary fibre, pectin, minerals: potassium, magnesium, calcium, phosphorus, iron, zink, copper, manganese; vitamins: b-Carotene, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, C, H, E; carbohydrates. As an average 100 g pollen contains: 20 g protein, 60 g carbohydrates 8 g fat and approx. 300 calories.
Read more about The Bee Pollen Composition
 Types of bee pollen and therapeutic benefits:
Types of bee pollen and therapeutic benefits:
According to the flower of provenience, the pollen can be of different types. This is important because such a unifloral pollen has a constant composition and can thus be successfully used in nutrition and medicine.
Bee pollen is low in calories but rich in proteins. It is antibacterial, anti-fungal, antioxidant, radiation-protective and hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-osteoporosis, anti-diarrhoea, immunomodulating, probiotic and prebiotic, anti-aging, antiatherogenic. Its ability to rejuvenate the body stimulates organs, enhances vitality, and accelerates the rate of recovery makes it a very popular tonic among sportsmen.
Antimicrobial activity:
Different studies have been made and showed the following:
– Pollen gathered from Ranunculus sardous and Ulex Europeans has shown antibacterial activity against: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphilococcus Aureus and S. Epidermidis
– Turkish pollen has an inhibitory effect against 13 different bacterial species pathogens for plants.
– Brazilian pollen has antibacterial activity against: Staphilococcus Aureus, Bacillus Subtilis, Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Klebsiella Sp.
Pollen also has similar antibacterial components as found in propolis and honeycombs, which are active against Streptococcus Viridans.
Antioxidant activity:
An antioxidant is a molecule capable of slowing down or preventing the oxidation of molecules. Nowadays, medicine says that oxidative stress leads to the development of chronic and degenerative diseases like cancer, autoimmune disorders, aging, cataracts, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, etc.
The antioxidant activity in pollen compared to that in most vegetables and fruits is 200 to 1000 times higher.
This activity depends on the flower species and geographic origin. Among the flowers that lead to pollen with very high antioxidant activity are Matricaria, Salix and Cistus Ladaniferus (and Incanus) (see images below).

Anti-radiation and hepatoprotective properties:
The pollen has an anti-radiation effect exactly like that of beta-carotene oil, the studies reported. Cistus Ladaniferus pollen proved to have the highest effect.
With a powerful hepatoprotective effect: Cardus and Castanea.
Chemopreventive and anticancer activity:
Pollen contains the following flavonoids: quercetin, rutin, chyrisin. There have been a lot of studies and research, which included: Brassica, Salix Alba, Cystus Incanus, Rosa Rugosa.
Antiinflamatory activity:
Inflamation of tissues and cells is caused by biological or physical agents and free radicals. The Pine Densiflora pollen has antinociceptive and antiinflamatory properties. The same activity was detected in Cistus pollen originated in Spain.
Anti-osteoporosis activity:
Osteoporosis is a reduced bone strength due to a reduction in bone mass/arhitecture that increases the fracture risk. The Cistus Ladaniferus was proven to have stimulatory effects on bone formation (in vitro). For this, pollen was dissolved in water.
Anti-anaemia activity:
A reduced number of red cells was increased using 10 g/kg/ day of multifloral bee pollen.
Anti-diarrheal activity:
Eucaliptus globulus and Salix atrocinerea.
Anti-allergenic activity:
In folk medicine, pollen was always used in small doses to heal hay fever, but recently, allopathic medicine confirmed that some flavonoids in pollen exert anti-allergic and anti-hay fever effects. There are some vaccines and drugs that have been made, and many others are in testing.
Gramineae pollen vaccine against hay fever has proved very good results so far.
Aqueous pollen extract was used with great success in house-dust asthma.
Pollysat decreases the symptoms of hay fever.
Homeopathy also uses grass pollen preparations in treating hay fever.
Immunomodulator : especially Brassica bee pollen
Probiotic & Prebiotic activity, Anti-aging.
Uses of unifloral pollen in folk medicine:
Antibiotic: Eucalyptus, maize, chestnut, dandelion, clover
Improves blood circulation: cherry, horse chestnut, sweet chestnut, willow
Heart fortification: hawthorn, apple
Calming & against sleeplessness: acacia, citrus, hawthorn, linden, poppy
Cough: poppy
Diuretic: dandelion, cherry, cornflower
Digestive (including tumors): acacia, lavender, rosemary, wild rose,
Improvement of liver function: horse chestnut, sweet chestnut, and dandelion
General tonifier: apple, eucalyptus, willow
Ulcer healing: rape
The pollen is also used to treat alcoholism.
See also:
Sweet chestnut and blackberry pollen
Willow pollen
Wild Rose pollen
Plum pollen
Heather pollen
Contraindications:
– some neuropsychiatric diseases: sexual hyper-excitability, nymphomania, advanced cerebral atherosclerosis and mania;
– some endocrine diseases: pituitary hyper-function, adrenal, thyroid, testicular and female virilization;
– certain metabolic disorders: obesity, excess of cholesterol and lipids in blood, and diabetes;
– specific allergies.
Prophylactic dose:
Adults: 2 teaspoons daily (approx. 10 -15 g);
Children (2-6 years old): 1 teaspoon daily (5 g).
This dose can be taken for 3 months a year, during the winter.
Therapeutic dose:
Adults: 20-50 g daily, taken 3 times a day, 1-2 hours before meals.
For better digestibility, pollen must be soaked in water over night (or for a few hours). If it is not soaked, make sure you chew it very well. It can also be mixed with honey.
There are other apitherapists who recommend taking pollen after meals, like this:
adults: 30-40 g (4-6 teaspoons) pollen (or 12-20 g beebread) daily for 3 days, then half this dose for another 2-6 weeks.
children: 0.4-0.6 g pollen (or 0.2-0.3 g beebread) per kg body weight, daily, for the first 3 days and then half the dose for 2-6 weeks. After a one-month break, the treatment can be taken again.
1 teaspoon = 6 g bee pollen
1 dessertspoon = 9 g bee pollen
1 tablespoon = 12 g bee pollen
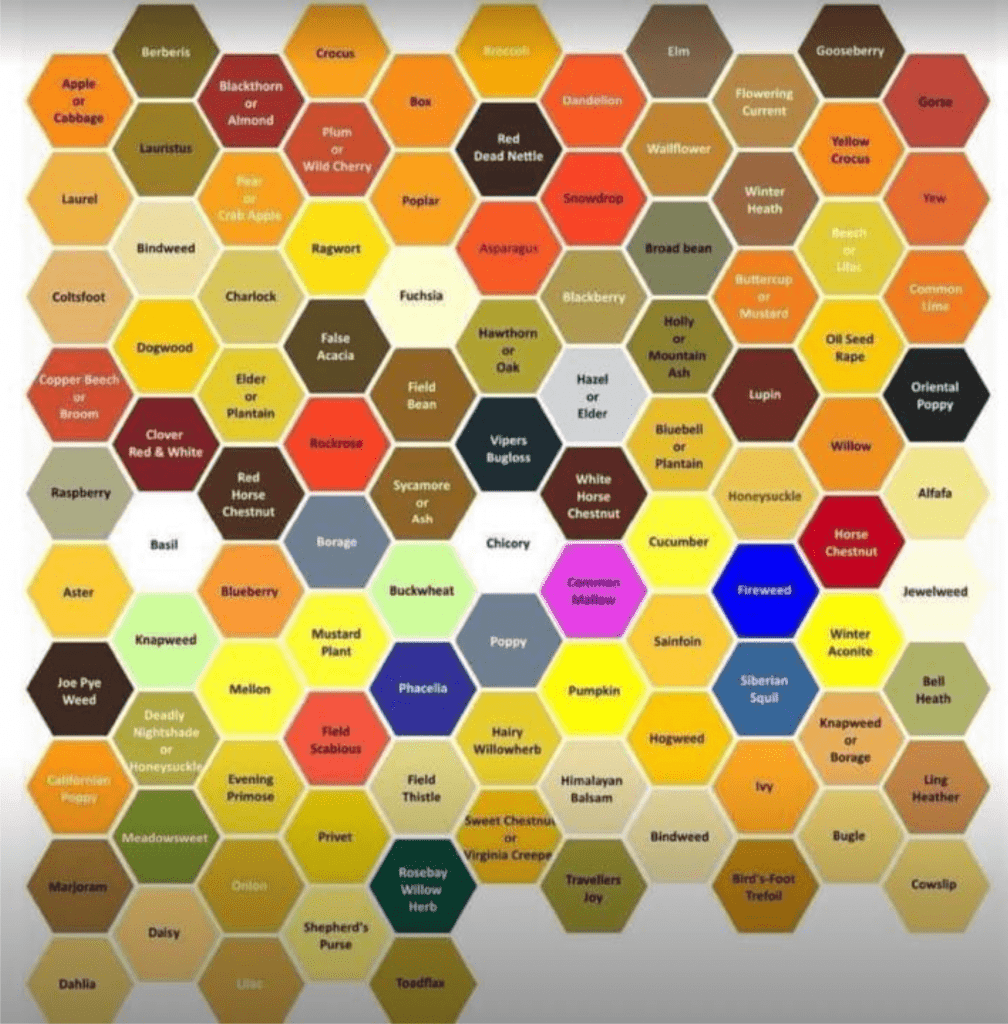
Pollen has lots of colors, depending on its source. Here is a chart of the most representative.
A bit of history:
 In 5000 BC, an Egyptian papyrus described the pollen as “a life-giving dust.”
In 5000 BC, an Egyptian papyrus described the pollen as “a life-giving dust.”
Hippocrates and Pliny the Elder also called Fathers of Western Medicine, recognized the healing qualities of bee pollen and prescribed it to their patients.
In new times, bee-collected pollen began to be used for human nutrition only after the Second World War.
info references:
Fanica Voinea Ene, Sa ne tratam singuri, Ghid de terapie naturista, 2006.
Stefan Bogdanov, Bee Product Science, february 2014, www.bee-hexagon.net
Tichy, J.Novak, J (2000) Detection of antimicrobials in bee products with activity against viridans streptococci. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 6
Carpes, S T, Begnini R, De Alencar SM, Masson ML (2007) Study of preparation of bee pollen extracts, antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Ciencia e Agrotecnologia 31
Erkmen O, Ozcan MM (2008) Antimicrobial effects of Turkish propolis, pollen, and laurel on spoilage and pathogenic food-related microorganisms. Journal of Medicinal Food 11
Taylor M, Reilly D, LLewellyn R, MCSharry C, Aitchison T (2000) Treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis using homeopathic preparation of common allergens in the southwest region of US: A randomized controlled clinical trial.